Alphabet Knowledge
Alphabet knowledge is the understanding that speech sounds and words can be represented using a sound-symbol system, known as a grapheme-phonemic system. Students must learn the shapes of letters, the letter names, the letter sounds, and then “which shapes correspond to which names and sounds” (Shmidman & Ehri, 2010). In learning to read, children must deciper the print before they can comprehend the meaning of the print. To achieve fluency in reading, which allows the reader to focus more of their attention on understanding the message conveyed in text, the deciphering of print needs to become automatic (Ehri, 2008).
Alphabetic Principle's Big Ideas
Orthographic Mapping
Orthographic mapping is the cognitive process by which the sight of a given word activates its pronunciation, spelling, and meaning from memory. “The speed and ease with which words are retrieved from the orthographic lexicon depends on the degree to which these three forms are linked - or ”bound" - to one another in memory" (https://www.ldatschool.ca/orthographic-mapping/#).
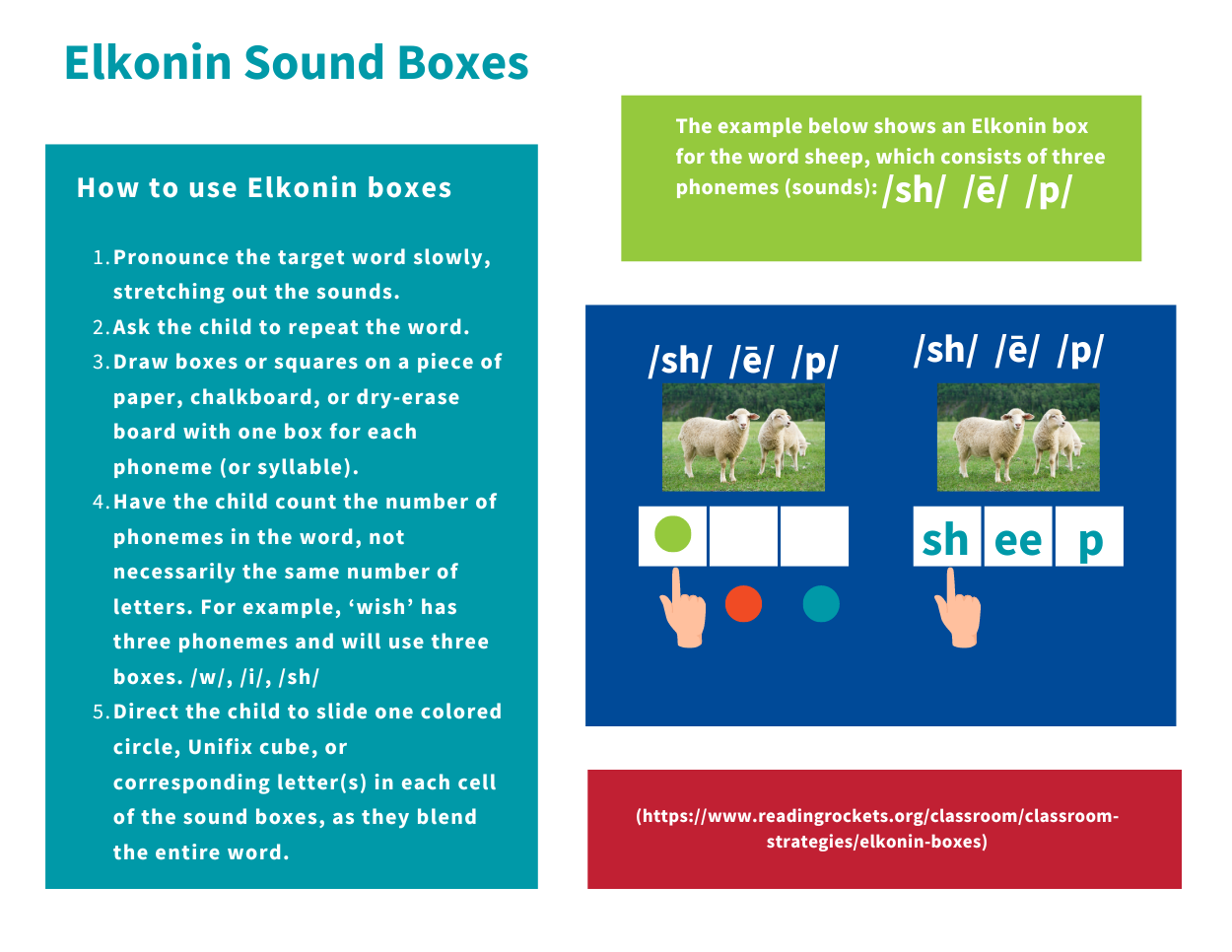
Elkonin sound boxes are a tool often used in early literacy instruction to help children analyze and ‘map’ the correct phoneme sound onto its corresponding letter(s).
Phonemic Awareness Skills versus Phonics
Phonemic Awareness skills precede phonics skills because children must first develop an understanding of how spoken language maps to written language. Whereas, phonics is the ability to apply letter-sound knowledge when translating print into speech. Phonics provides readers with a tool to unlock or ‘decode’ the pronunciation of written words.
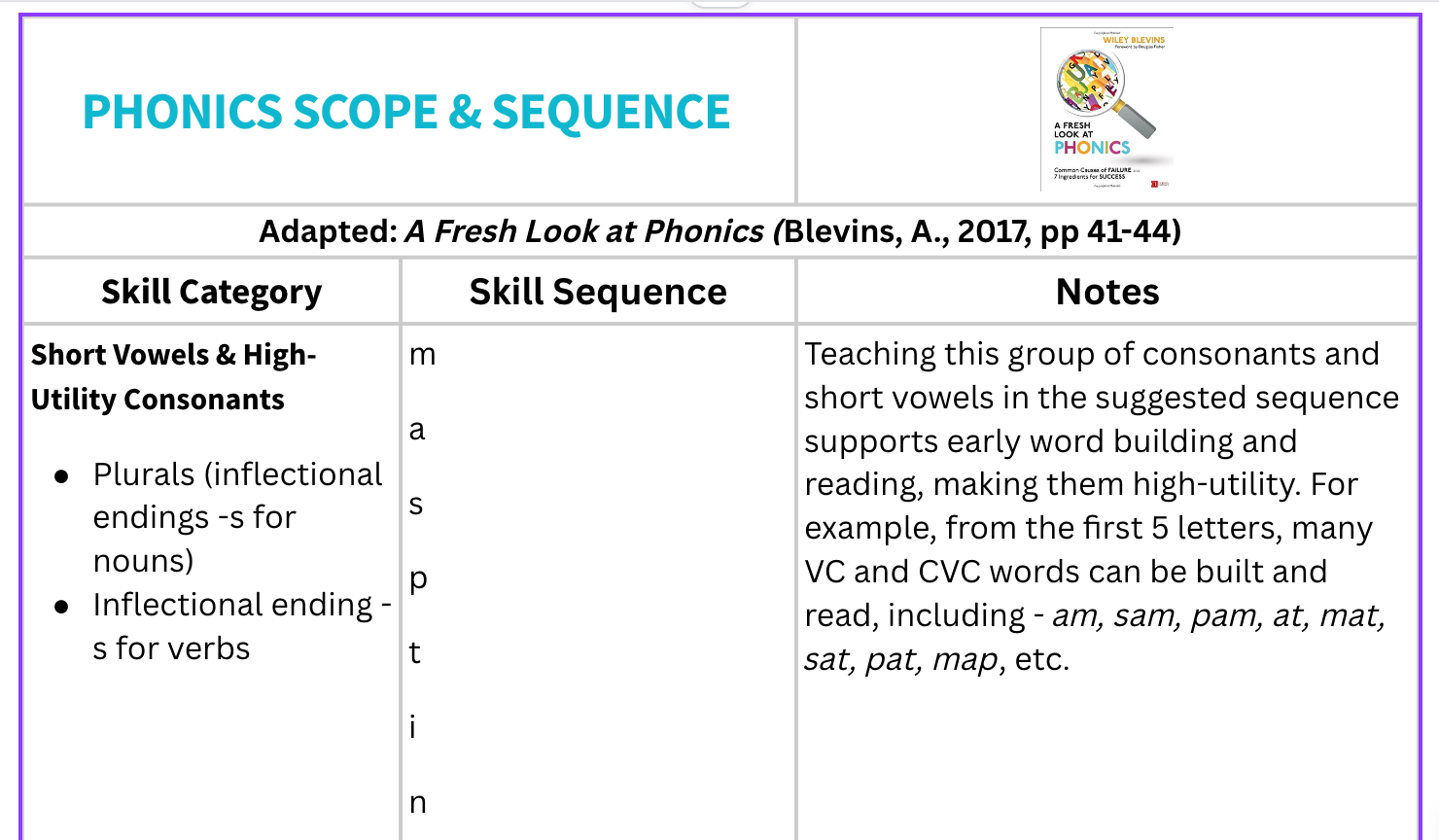
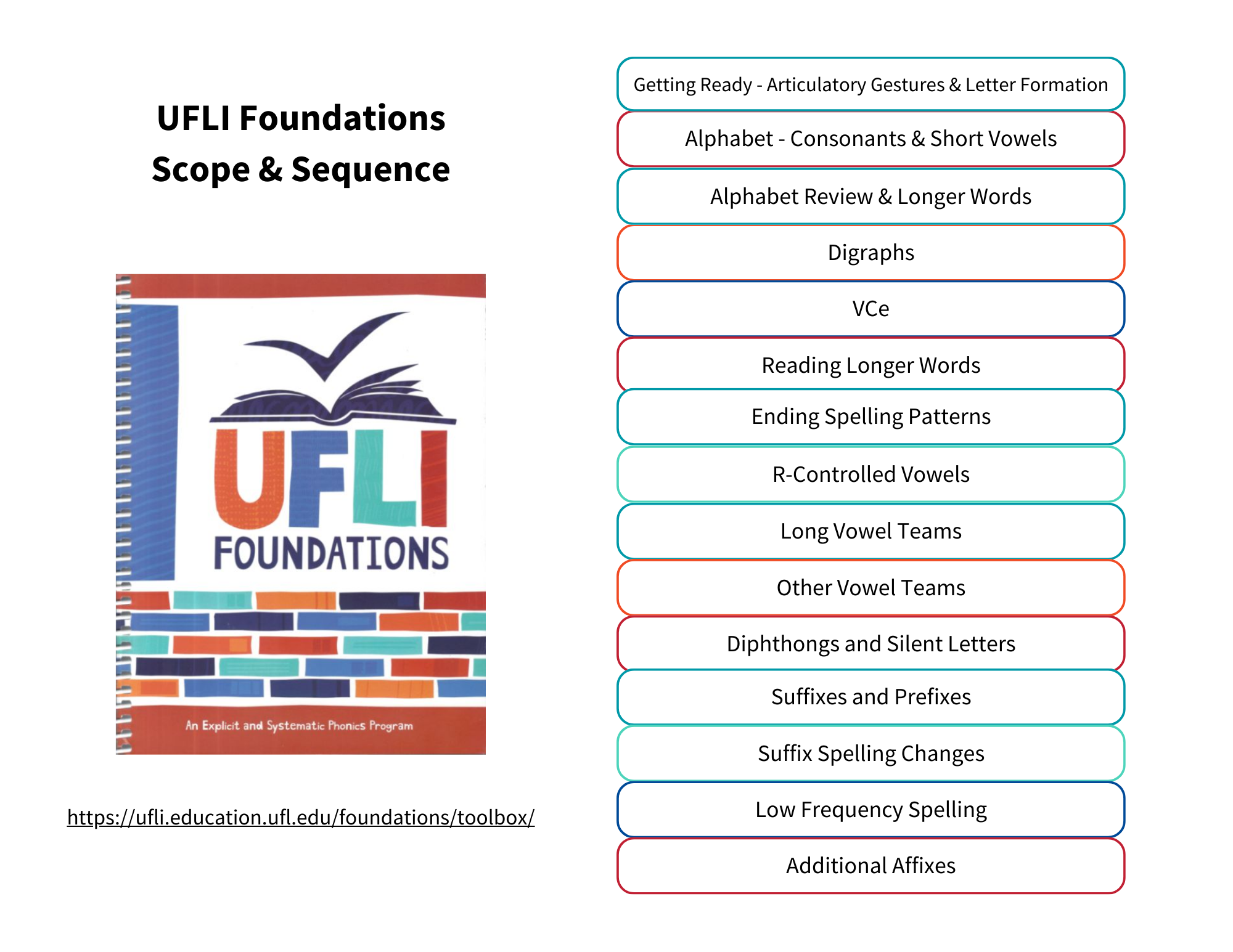
Phonics Scope & Sequence Models that Inform our PracticeNote: You may find slight variations in the order of skills taught within different phonics scope & sequence processes. Regardless of which tool you select to use, it is most important that phonics lessons be delivered in an explicit and systematic way. | ||
Wiley Blevins: A Fresh Look At Phonics | UFLI Foundations | Shifting the Balance (K to 2) |
 |  |  |
The Role of Decodable Books
Skilled reading requires both decoding and comprehension abilities for students to become proficient readers. Students need access to a variety of texts for different instructional purposes. Decodable texts support explicit phonics lessons by providing reading application practice of newly learned skills. Phonics instruction needs to be explicit and systematic, following a clearly defined scope and sequence that includes mastery assessments throughout the learning cycle. Decodable texts play a integeral part in building and solidifying a student's understanding that there are predictable letter-sound patterns in reading and writing.
Considerations to Think About When Selecting and Using Decodable Text - (Shifting The Balance, Jan and Kari, 2024)
| Exploring Decodable Texts | What, Why, Who… | How many? | What to Look For; The Words |
 |  |  |  |
| What Else to Look For: The Meaning | What About Free Decodable Books and Texts | More Ideas for Getting Started | |
 |  |  |

Key Resources: What Informs Us?
Alphabet Knowledge and Phonics
- abc desk size template - student resource /documents/08395cfb-1390-4930-ab9b-99d13bcdfd18
- A Fresh Look at Phonics, Wiley Blevins (2017) http://www.wileyblevins.com/
- Letter Lessons and First Words, Heidi Mesmer https://www.heinemann.com/products/e10544.aspx
- Phonemic Awareness: Elkonin Sound Boxes activities increasing in complexity /documents/4f0c8f6e-a8b5-4f82-a5d0-b315a8a692aa
- Rime Magic by Sharon Zinke https://rimemagic.com/
- Shifting The Balance K-2 https://thesixshifts.com/
- The Phonics Companion: https://www.pearsoncanadaschool.com/pd/products/phonics-companion.html
- UFLI Foundations https://ufli.education.ufl.edu/foundations/
Decoding Coaching Cards - SD24 June 2024
High Frequency Words
- For more information about Orthographic Mapping visit: https://www.ldatschool.ca/orthographic-mapping/#
- Shifting the Balance - Sight Word Success is a course you may be interested in taking https://thesixshifts.com/sight-word-success/
- Shift 4: Revising High Frequency Word Instruction - Building words and Hearing Sounds pdf
- UFLI Foundations Game Generator for ‘Irregular Words’ (Scroll to the bottom of the page. The Generated Game boards use explicitly taught words from the lessons.) https://ufli.education.ufl.edu/foundations/apps/
Word lists:
- Dolch - https://sightwords.com/sight-words/dolch/;
- Fry - https://sightwords.com/sight-words/fry/
- SD23 Central Okanagan Public Schools: ELP List 1 https://www.sd23ltd.com/high-frequency-words-list-1 and List 2 https://www.sd23ltd.com/high-frequency-words-list-2
- Shifting the Balance - 109 Power Word List: https://thesixshifts.com/downloads-k-2/
- UFLI Heart Words from UFLI Foundations - https://ufli.education.ufl.edu/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/UFLI_Heart_Word_Printable_Cards.pdf
Shared Big Book lists (books can be requested through the DRC):
- Kindergarten Shared Reading Book List /documents/563b4075-2144-4cbb-9727-39311c85ee1e
- Grade 1 Shared Reading Book List /documents/f1d76bec-69cc-4821-8273-0530a3e0b727
- Grade 2 Shared Reading Book List /documents/8902da71-6398-4c30-a112-639c656a745d
- Grade 3 Shared Reading Book List /documents/275ec3cc-f328-42a8-b66a-041a266cd7e5
Words That Sing Blackline Masters:
- Words that Sing Kindergarten /documents/41b1daae-a4dc-418b-ae19-bd3602f607e1
- Words that Sing Grade 1 /documents/0b7d274e-b568-42a3-ad50-015fc35c8b9e
- Words that Sing Grade 2 /documents/b782b35c-403f-41a5-8325-4997d7411ff7
Key Resources: What Informs Us in French Immersion?
La phonétique
- Voir l’Appréciation de rendement en littératie précoce (ALP) SD22
- Calgary Board of Education Littératie structurée https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1XBmgJu9r6Gp8kOp-7Bxz21I9l_1LWx_a
- Raconte-moi l’alphabet (M) ; Raconte-moi les sons (1-3) ; Au village des sons (1-3) https://www.cheneliere.ca/2710-auteur-josee-laplante.html
- ClassImages : Enseigner les associations lettres-sons à partir des images (M-3) https://www.lexiegraphie.com/boutique
- Continuum de développement de la conscience phonologique et phonétique M-3 https://curriculum.novascotia.ca/node/651
- Shifting the Balance https://thesixshifts.com/
La littératie intégrée
- Modulo Littératie (M-3) https://www.cheneliere.ca/fr/modulo-litteratie-maternelle-et-1re-annee.html
Mots de haut-fréquence
- Voir l’Appréciation de rendement en littératie précoce (ALP) SD22
Lecture
- Voir l’Appréciation de rendement en littératie précoce (ALP) SD22
- Continuum de développement de la lecture M-3 https://curriculum.novascotia.ca/node/651
Les livres décodables
- Adorable et décodable https://www.iplusinteractif.com/contenus-statiques/extraits/adorable-decodable/index-en.html
- Décode https://passetemps.com/primaire/1255-decode-niveau-1-livrets-1-a-6.html
- Facile à lire (M-3) https://facilealire.com/en/
- Une syllabe à la fois (M-2) https://editionsmd.com/une-syllabe-a-la-fois
- Décode Habile (M-2) https://www.decodehabile.com/

